2. Therapeutics and assessment of treatment efficiency
Topical lead: Dr. Peter Nirmalraj
The cerebral accumulation of α-Synuclein (α-Syn) and amyloid β-1-42 (Aβ-42) proteins are known to play a crucial role in the pathology of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Currently, Levodopa (L-dopa) is the dopamine replacement therapy for treating bradykinetic symptoms visible in PD patients. There is emerging evidence that individuals with PD frequently exhibit non-motor symptoms typical of AD patients, with α-Syn and Aβ accumulations co-detected in the brain of PD and AD patients. Importantly, pathogenic processes triggering the onset of AD and PD typically occur several decades before the emergence of visible signs of memory and cognitive deficits, indicating that the gradual changes in α-Syn and Aβ protein structure from monomers, oligomers, and protofibrils to fibrils progressively disrupt neuronal function and connectivity. These pathological protein aggregates are present in both blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of PD and AD patients, which provides an opportunity to monitor disease progression before the onset of clinical symptoms through the development of fluid biomarkers aimed at the detection and quantification of α-Syn and Aβ-42 proteins.
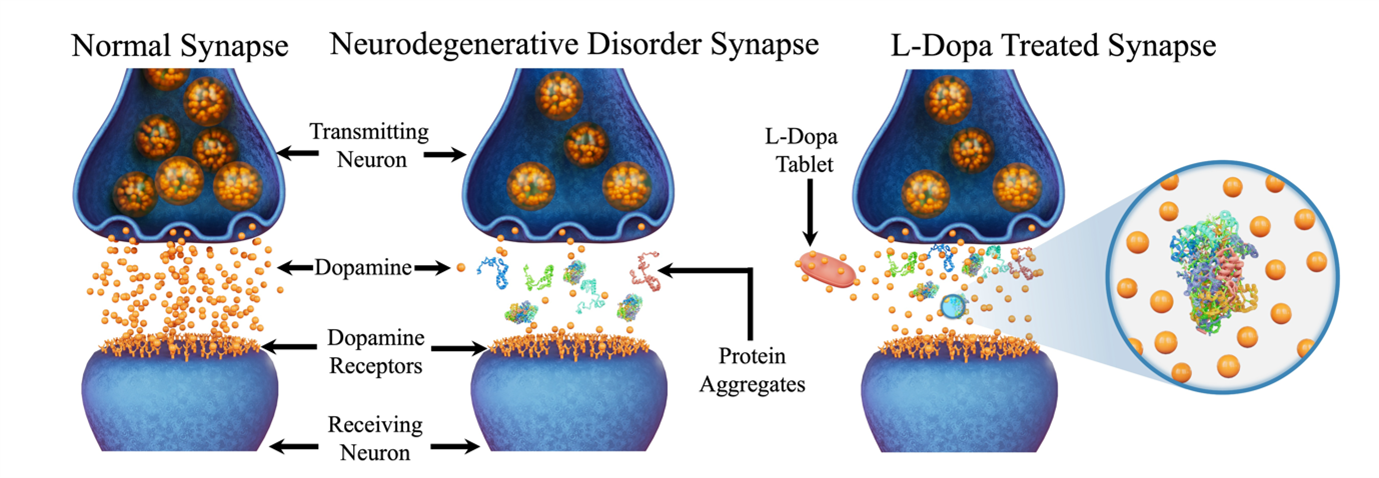
We employ nanoscale imaging and chemical spectroscopy-based approaches to study the concentration-dependent L-dopa effects on pathological proteins. Information obtained at nanometer length scales reveals intriguing details regarding changes to protein aggregate morphology and the onset of off-pathway oligomers.
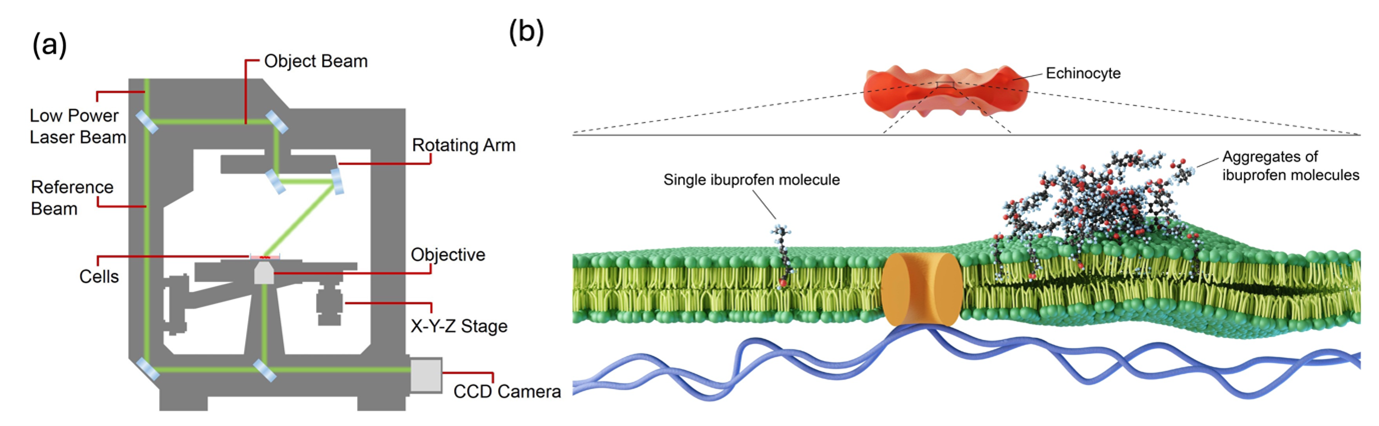
Using our world-class analytical techniques at Empa, we further attempt to understand the effect of various anti-amyloids (aducanumab) on proteins to over-the-counter drugs such as Ibuprofen on blood. Understanding the dose-dependent effect of over-the-counter drugs on red blood cells (RBCs) is crucial for hematology and digital pathology. Yet, it is challenging to continuously record the real-time, drug-induced nanoscopic shape changes of RBCs in a label-free manner. To address this topic, we use a digital holotomographic microscope to resolve the effect of ibuprofen on RBCs.