Interaction with environment
Thermodynamic modeling of the interaction with the environment
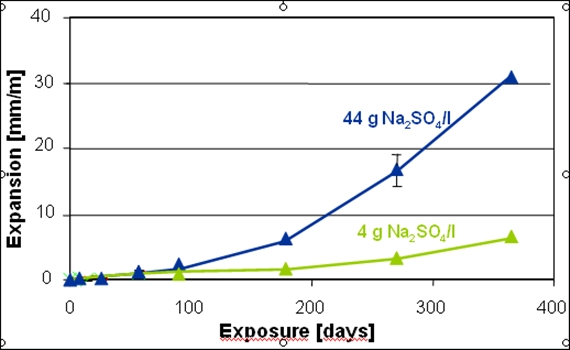
To test the “sulfate resistance” of a specific cement, mortar and concrete samples are generally submersed for a few weeks in concentrated Na2SO4-solutions and the mass and length gain is monitored as a function of time. High sulfate concentrations, as used in such tests, lead to the precipitation of gypsum, while lower sulfate concentrations, as present under field conditions, lead to no or only very little gypsum precipitation. The mortar samples show strongly differing expansion and mass gain depending on the reaction solution. Further factors influencing the expansion are the absence or presence of CO2 in the interacting solution, the amount of solution, the frequency of the exchange of the solutions, the sample geometry and the temperature. Considering all these factors it is not surprising that the tests carried out in different laboratories show large variations. In addition, the correlation of the test results with expansion and deterioration under field conditions is poorly understood.
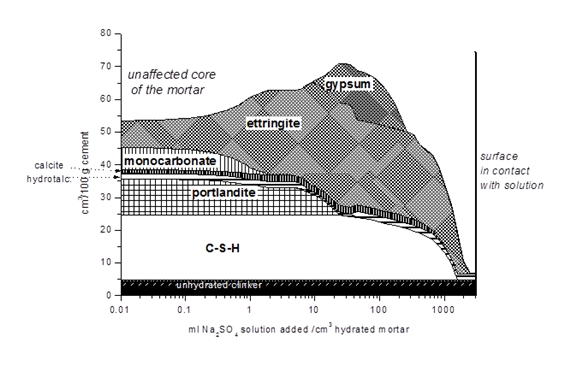
The combination of thermodynamic modelling with experimental techniques such as XRD, SEM/EDS enables us to gain more insights into the process governing the interaction with the environment on a chemical level. Our studies in recent years focused on the effect of sulfate, chloride, carbonate and on alkali silica reaction.
Important publications
- Kunther, W., Lothenbach, B. (2018) Improved volume stability of mortar bars exposed to magnesium sulfate in the presence of bicarbonate ions. Cement and Concrete Research, 109, 217-229 3. Kunther, W., Lothenbach, B. (2018) Improved volume stability of mortar bars exposed to magnesium sulfate in the presence of bicarbonate ions. Cement and Concrete Research, 109, 217-229
- Hargis, C., Lothenbach, B., Müller, C., Winnefeld, F. (2017) Carbonation of calcium sulfoaluminate mortars, Cement and Concrete Composites, 80, 123-134.18. Hargis, C., Lothenbach, B., Müller, C., Winnefeld, F. (2017) Carbonation of calcium sulfoaluminate mortars, Cement and Concrete Composites, 80, 123-134.
- Shi, Z., Geiker, M.R., De Weerdt, K., Østnor, T., Lothenbach, B., Winnefeld, F., Skibsted, J. (2017) Role of calcium on chloride binding of hydrated Portland cement – metakaolin limestone blends, Cement and Concrete Research, 95, 205-216.
- Leemann, A., Pahlke, H., Loser, R., Winnefeld, F. (2018). Carbonation resistance of mortar produced with alternative cements, Materials and Structures 51,114
- Leemann, A., & Moro, F. (2017). Carbonation of concrete: the role of CO2 concentration, relative humidity and CO2 buffer capacity. Materials and Structures, 50(1), 30.
- Loser, R., & Leemann, A. (2016). An accelerated sulfate resistance test for concrete. Materials and Structures, 49(8), 3445-3457
- Leemann, A./Loser, R. Analysis of concrete in a vertical ventilation shaft exposed to sulfate-containing groundwater for 45 years. Cement & Concrete Composites 2011, 74–83
- Leemann, A./Lothenbach, B./Thalmann, C. Influence of superplasticizers on pore solution composition and on expansion of concrete due to alkali-silica reaction. Construction and Building Materials 2011, 25(1), 344-350.
- Leemann, A./Le Saoût, G./Winnefeld, F./Rentsch, D./Lothenbach, B. Alkali–silica reaction: the influence of calcium on silica dissolution and the formation of reaction products. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 2011, 94(4), 1243-1249.
- Leemann, A.,Lothenbach, B.,Siegrist, H.,Hoffmann, C. Influence of water hardness on concrete surface deterioration caused by nitrifying biofilms in wastewater treatment plants. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation 2010, 64(6), 489-498
- Loser, R., Lothenbach, B., Leemann, A., Tuchschmid, M. (2010) Chloride resistance of concrete and its binding capacity – comparison between experimental results and thermodynamic modeling. Cement and Concrete Composites, 32(1), 34-42.
- Schmidt, T., Lothenbach, B., Romer, M., Neuenschwander, J., Scrivener, K. (2009) Physical and microstructural aspects of sulfate attack on ordinary and limestone blended Portland cements. Cement and Concrete Research, 39(12), 1111-1121.

Prof. PD. Dr. Barbara Lothenbach
Senior Researcher / Projektleiterin / Adjunct Prof. NTNU

-
Share
