XPCI & XDFI
In these novel methods the image contrast is not based on X-ray attenuation, but on their phase shift (or refraction) and ultra-small-angle scattering. X-ray phase contrast images are especially useful for light materials, which show little X-ray attenuation contrast. Dark-field or scattering images are beneficial for highly structured, porous structures like fibre reinforced plastics, paper, textiles or foams, where structural elements of sub-resolution sizes can be detected.
Propagation-based Imaging
Propagation-based phase-contrast imaging is the bas-line option on many synchrotron beam lines. With the availability of micro/nano-focus X-ray tubes and high-resolution imaging detectors, this technique found its way to the laboratory. Our RX Solutions Easy Tom XL micro/nano-CT scanner with its tubes and detectors and the flexibility of their combinations enables high-resolution propagation-based imaging. Phase retrieval can be performed using the Paganin method or the modified Bronnikov method and Bronnikov aided-Correction method.
Phase Contrast and Dark-Field Imaging Systems:
Speckle-based imaging systems
Speckle-based imaging add-ons have been developed or our micro-CT and Easy Tom XL scanners.
Grating based imaging systems
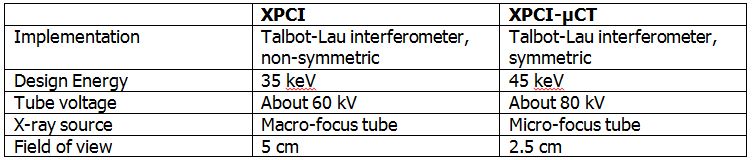
Empa has two grating-based systems available, which allow for a simultaneous acquisition of a differential phase-contrast image, a dark-field or scattering image and the classical transmission image. These setups can be used for single radiographies or in CT mode. X-ray Talbot-Lau interferometer for phase-contrast and scattering imaging with a macro-focus source for fast image acquisitions:
X-ray Talbot-Lau interferometer for phase-contrast and scattering imaging with a macro-focus source for fast image acquisitions:
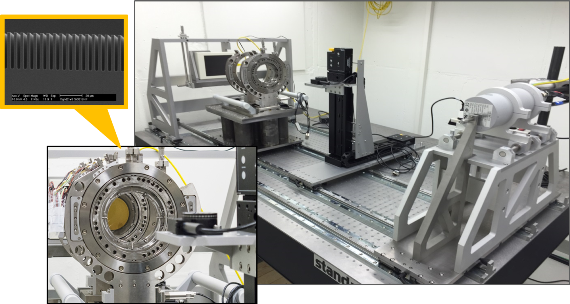
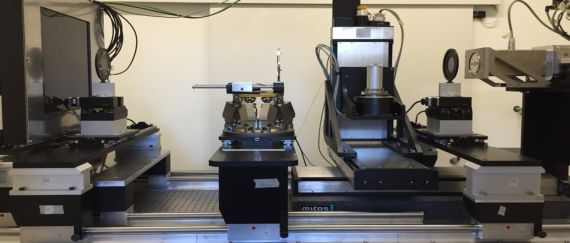
X-ray Talbot-Lau based on a micro-focus CT setup:

-
Share
