Advancement Analytical Techniques
APRECON-GC-ToF-MS
The APRECON-GC-ToF-MS builds on the expertise gained at Empa with the previous generation Medusa system, which has been in operation for more than 10 years at the Jungfraujoch high altitude research site. The following aspects have been significantly improved:

- efficient cooling of the two cryotraps, using state-of-the art Stirling cooling technology. This allows to trap more completely compounds of high volatility (low boiling point), and therefore leads to more accurate data and lower detection limits.
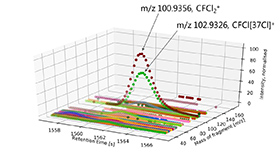
- largely improved mass resolution of the detector, shifting from the traditional quadrupole mass spectrometer technology (mass resolution of one) to time of flight technology (Tofwerk, Thun, Switzerland). The mass resolution is now better than 3000, allowing much more selective measurements of each mass peak.
- This new analytical system allows for simultaneous screening of virtually all masses from zero to 300 m/z (or even more), therefore recording both known and unknown trace gases, all present in the atmosphere. The obtained dataset therefore constitutes a unique and unprecedented digital archive of the atmosphere, allowing future screening of yet unidentified compounds.
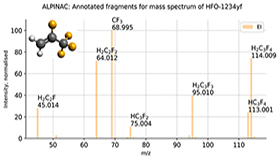
ALPINAC (ALgorithmic Process for Identification of Non-targeted Atmospheric Compounds): A software tool for automatic fragment formula annotation of EI-TOF-MS spectra.
Empa's APRECON-GC-TOF-MS, operating in the range of about 20 m/z to 300 m/z, with mass resolution better than 3000, measures mass spectra of pre-concentrated air samples often containing several unidentified contaminants. Manual identification of these discovered compounds cannot keep up with the amount of information provided and requires computational methods. We have developed automated and reliable Python-based open-source software (ALPINAC) capable of annotating mass spectral peaks. Using this information, ALPINAC reconstructs the most likely formulas for the molecular precursor ion, even if it is not present in the measured spectra themselves.
ALPINAC works completely independently of mass spectral libraries and requires only experimental input variables, mainly the m/z position of the peak, the corresponding uncertainty, and the area of the peak.
It represents a universal tool for the detection and determination of unknown substances and its improvement is an ongoing research project in our group.
The method is explained in details in Guillevic et al., 2021
The source code can be freely downloaded here
Medusa GC-quadrupole MS

The Medusa system is currently set up to measure the following compounds:
- CFCs: CFC-11, CFC-12, CFC-13, CFC-113, CFC-114, CFC-115.
- HCFCs: HCFC-22, HCFC-141b, HCFC-142b, HCFC-124
- Halons H-1301, H-1211, H-2402
- CH3Cl, CH3Br, CHCl3, CH3CCl3, CCl4, TCE, PCE
- HFCs: HFC-23, HFC-32, HFC-134a, HFC-152a, HFC-125, HFC-143a, HFC-227ea, HFC-365mfc, HFC-245fa, HFC-236fa.
- HFOs: HFO-1234yf, HFO-1234ze(E), HCFO-1233zd(E)
- PFC and other fluorinated compounds: PFC-116, PFC-218, PFC-318, SF6, CF4, (SF5CF3)
- Hydorcarbons: C2 – C6 hydrocarbons
- Carbonyl sulfide (OCS), SO2F2
- and more ….
-
Share