Data-driven emission quantification
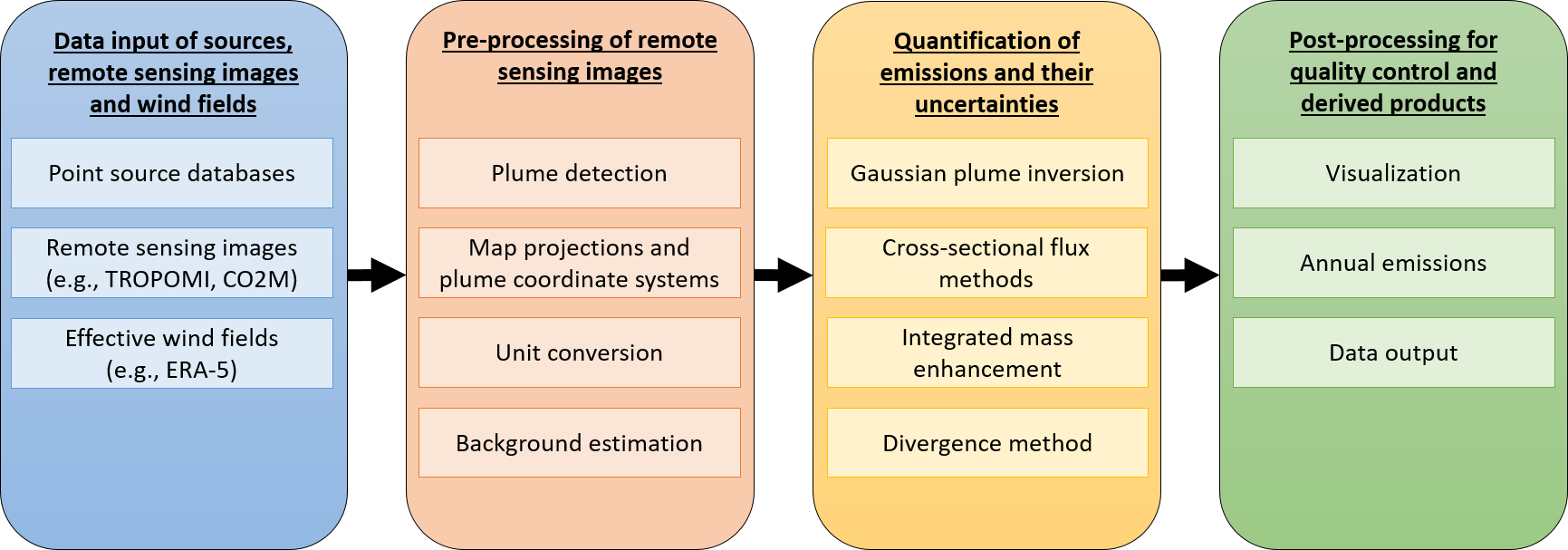
We develop data-driven tools for quantifying anthropogenic emissions of cities, power plants and industrial facilities. Our tools include mass-balance approaches and machine learning models. We maintain the open-source Python library for data-driven emission quantification (ddeq).

Publications
- Meier et al.: Quantifying NOX emissions of point sources from NO2 satellite observations, EGUsphere [prepint], doi: 10.5194/egusphere-2024-159, 2024.
- Koene et al.: On the theory of the divergence method for quantifying source emissions from satellite observations, ESS Open Archive [preprint], doi: 10.22541/essoar.169447417.79649337/v1, 2024
- Kuhlmann et al.: The ddeq Python library for point source quantification from remote sensing images (Version 1.0), EGUsphere [preprint], doi: 10.5194/egusphere-2023-2936, 2024
- Hakkarainen et al.: Analyzing nitrogen dioxide to nitrogen oxide scaling factors for computationally light satellite-based emission estimation methods: a case study of Matimba/Medupi power stations in South Africa, Atmos. Pollut. Res., doi: 10.1016/j.apr.2024.102171, 2024.
- Dumont Le Brazidec et al.: Deep learning applied to power plant emissions quantification using XCO2 synthetic satellite images, Geo. Model. Dev., doi: 10.5194/gmd-17-1995-2024, 2024.
