Observing system simulation experiments
Observing System Simulation Experiments (OSSE) are modeling studies to evaluate the value and guide the development of new instruments prior to building the full system. We use state-of-the-art atmospheric transport models to simulate current and future remote sensing systems from which we generate realistic synthetic observations.
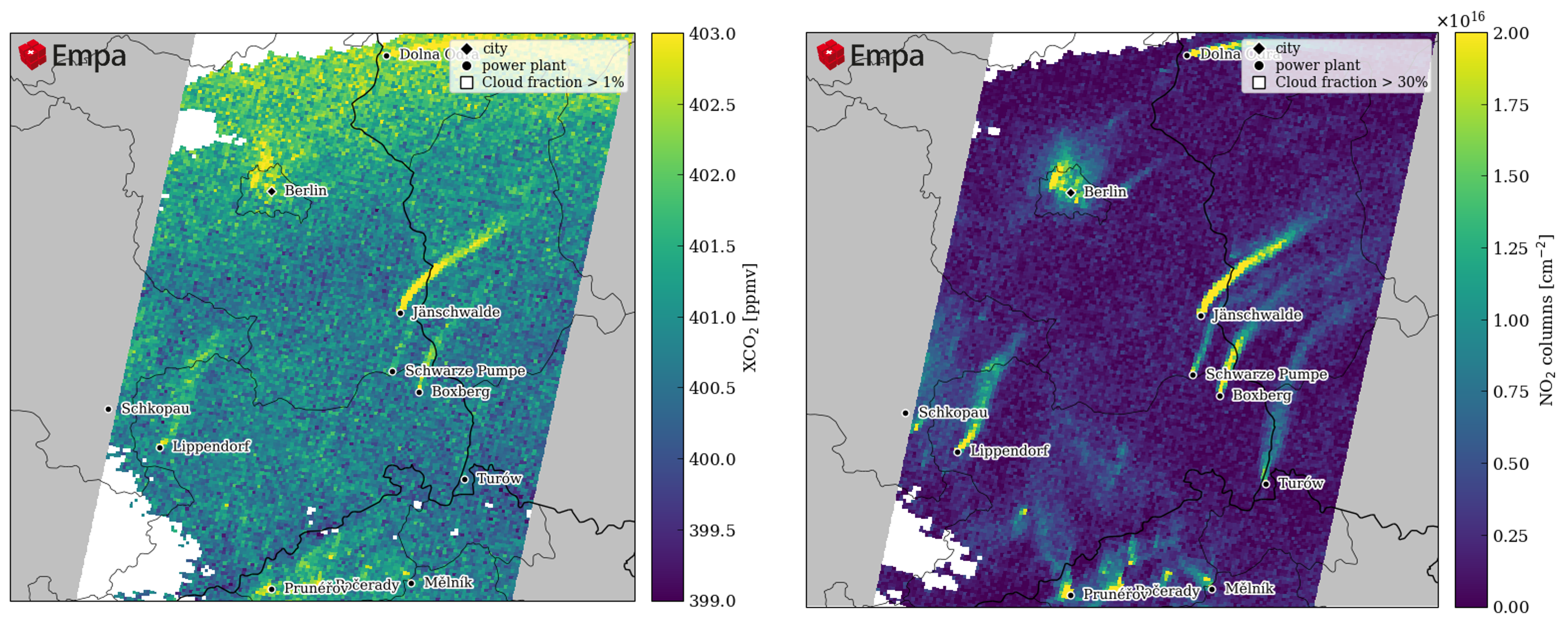
Example of CO₂ and NO₂ image observed by CO2M satellite. The images were generated from high-resolution simulations with the COSMO-GHG model.

Publications
- Meier et al.: Quantifying NOX emissions of point sources from NO2 satellite observations, EGUsphere [prepint], doi: 10.5194/egusphere-2024-159, 2024.
- Koene et al.: On the theory of the divergence method for quantifying source emissions from satellite observations, ESS Open Archive [preprint], doi: 10.22541/essoar.169447417.79649337/v1, 2024
- Kuhlmann et al.: The ddeq Python library for point source quantification from remote sensing images (Version 1.0), EGUsphere [preprint], doi: 10.5194/egusphere-2023-2936, 2024
- Hakkarainen et al.: Analyzing nitrogen dioxide to nitrogen oxide scaling factors for computationally light satellite-based emission estimation methods: a case study of Matimba/Medupi power stations in South Africa, Atmos. Pollut. Res., doi: 10.1016/j.apr.2024.102171, 2024.
- Dumont Le Brazidec et al.: Deep learning applied to power plant emissions quantification using XCO2 synthetic satellite images, Geo. Model. Dev., doi: 10.5194/gmd-17-1995-2024, 2024.
