LIB-SARS project – Support the development of a Swiss industry-led take-back system of Lithium-Ion Batteries from the automotive sector
In this context, the LIB take back and disposal project of SARS (Foundation Auto Recycling Switzerland) aims to support this effort by designing several LIB reverse logistics and recycling system variants, test their behaviour against multiple possible evolution scenarii using computer models, and compare the simulation results in order to provide useful insights to the sectoral stakeholders.
The model is realized based on the dynamic Mass Flow Analysis (MFA) method that allows to evaluate the future end of life LIB flows, as well as the materials they contain. Recycling is also part of the model, which allows quantifying how the materials composing the LIBs spread through different treatment technologies. A system dynamics (SD) model is used to analyse and compare different financing possibilities of the system. Possible evolution scenarii include variation in availability in critical raw material necessary for battery manufacturing, different future market sharing among vehicle technologies, changing mobility habits of the Swiss population, etc.
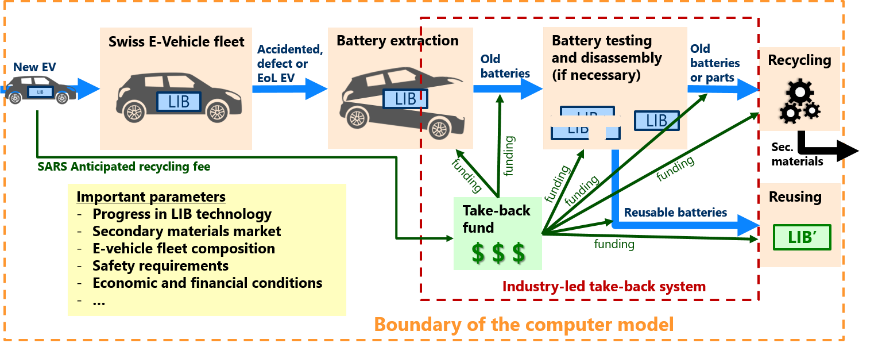
Figure: Conceptual representation of a reverse logistics system and its model
A comparative analysis of all the tested variants will help to identify the best system candidates, anticipate the volumes of end of life LIB and materials they contain to be recycled, as well as to estimate the overall costs. Those results are essential for the stakeholders to then implement a realistic and efficient reverse logistics and recycling system.
-
Share
