
Never miss an issue
Subscribe to our magazine
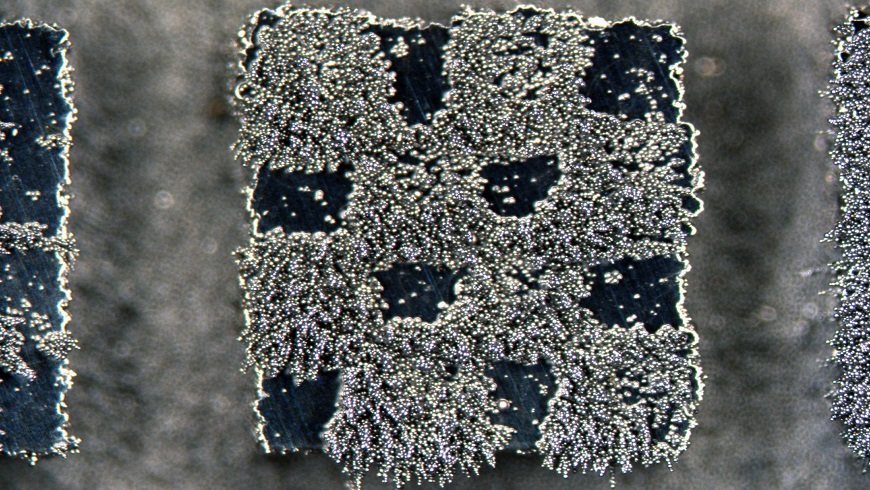
Metal 3D laser printing
Hot off the Oven
During metal processing in the 3D laser printer, temperatures of more than 2,500 degrees Celsius are reached within milliseconds, causing some components of the alloys to evaporate. While widely considered a problem inherent to the process, Empa researchers spotted an opportunity – and are now using the effect to create new alloys with novel properties and embed them in 3D-printed metallic work pieces with micrometer precision. More.

Insights
World Premiere in Bridge Construction
A milestone for an extremely versatile material with Swiss roots: On 3 May 2020, a 127-meter long railway bridge was pushed over the A8 motorway near Stutt-gart. It is the first bridge whose 72 suspension cables are made entirely of carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP). This ultra-light yet extremely stable material was developed largely at Empa and has since been used in more and more structures. Image: L. Haspel, sbp Stuttgart
In Brief

“REMASK”: Joining Forces against the Mask Emergency
During the Corona crisis, protective masks have become a rare commodity. In order to equip Switzer-land with efficient protective material in future pandemic times, Empa researchers are working on the “ReMask” project together with a national consortium of research, health care and industry: new mask types and technologies for the reuse of existing protective material are being developed – for now, but also for future pandemics. In addition, information on the manufacture of masks and textile protective systems and information on standardized test methods have already been made publicly available.

Superconductivity at Room Temperature?
A research team from Switzerland, the USA and Poland has demonstrated a uniquely high density of hydrogen atoms in a metal hydride. The smaller distances between the atoms could allow significantly more hydrogen to be packed into the material – up to a point where it could become a superconductor at room temperature and normal pressure.

A Biosensor for the Covid-19-Virus
A team of researchers from Empa, ETH Zurich and Zurich University Hospital has succeeded in developing a novel sensor for detecting the new coronavirus. In future it could be used to determine the concentration of the virus in the environment – for example in places where there are many people or in hospital ventilation systems.

Sea Mussel Glue for Heart Muscles
If the heart muscle is damaged, repairing the constantly active organ is a challenge. Empa researchers are therefore developing a tissue adhesive inspired by nature which can perfectly reattach defects in muscle tissue. They have taken advantage of the phenomenal adhesive power of sea mussels.

Circuits on all kinds of material
The Transistor out of the Printer

High-tech clothing
Wearable Health
There is more than cool looks about hip clothing for top performance: Thanks to a variety of smart technologies, high-tech clothing today is capable of analyzing body functions or actively optimizing the microclimate. The basis of these novel textiles are “smart” fibers and biocompatible composites that also contribute to innovations in biomedical research such as sensors, drug delivery systems or tissue engineering. More.
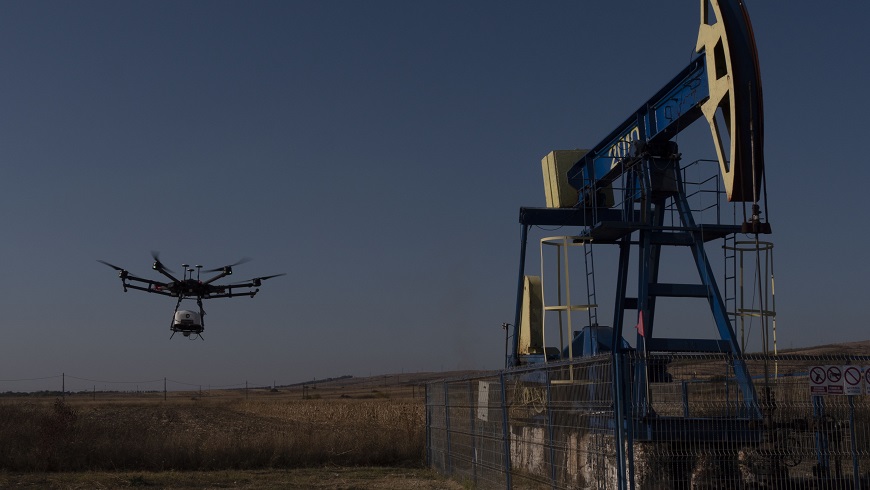

Mobile measuring instruments
Caught in flight
Humans are exposed to numerous harmful environmental influences, and it is an international concern to quantify these emissions as accurately as possible in order to be able to take measures to contain them. Empa is also part of these efforts and has, among other things, developed a drone equipped with state-of-the-art measuring instruments which can detect methane leaks. It is also assisting the European Space Agency (ESA) in the development of new satellites capable of detecting CO2 sources from space. More.
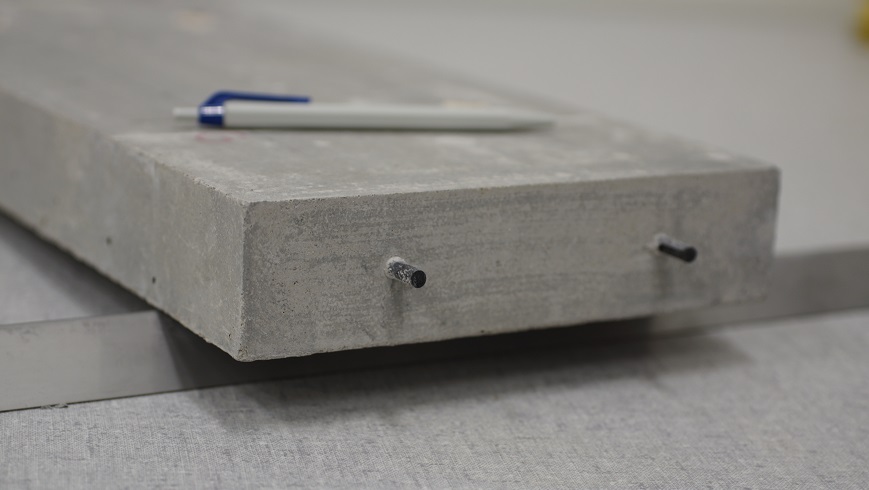

Cost-effective and material-saving
When Concrete learns to pre-stress itself
Concrete is by far the most widely used building material in the world – and the trend is rising. Using a new type of concrete formula, an Empa team has succeeded in producing self-prestressed concrete elements. This innovation makes it possible to build lean structures much more cost-effectively – and save material at the same time. More.

Against Food-Waste
Platinum keeps Fruit fresh
If different types of vegetables and fruits are stored together, they influence each other in the ripening process. This is due to ethylene, which is emitted by some plant-based foodstuff and accelerates ripening. To prevent excessive food waste due to accelerated ripening Empa and ETH Zurich researchers are developing a new catalyst that degrades ethylene into water and carbon dioxide. More.

TwingTec part of the Solar Impulse Foundation
Fresh Breeze for Ecology and Economy
The Solar Impulse Foundation is looking for 1000 solutions that will boost the economy - and protect the environment at the same time. The Empa spin-off TwingTec has made it onto the list: it is now part of Bertrand Piccard's #1000solutions of the Solar Impulse Foundation. More.

What comes after the lithium-ion battery?
Wanted: The best Storage Battery
The demand for batteries to store renewable energy will grow drastically in the coming years. Could we develop more sustainable technologies to save precious natural resources, besides the familiar lithium-ion batteries? More.

Next generation lithium-ion battery
Europe's Response to Elon Musk
Over the next four years, five research institutes and six industrial companies from seven European countries will work together to find solutions for the next generation of lithium-ion batteries. Also on board as a partner is the Swedish company Northvolt, which intends to set up two large-scale production facilities (gigafactories) for vehicle batteries in Europe. More.
Inside Empa

Concrete and Asphalt Research expanded
Since March 2020 the new Concrete and Asphalt Laboratory has strengthened Empa’s research in the field of building materials. Innovative technologies and materials for sustainable production and use are particularly in demand in these specialist areas, as these two building materials, with an annual volume of more than 4.5 billion tonnes, account for by far the largest proportion of all materials used worldwide.

Swiss Solar Façade breaks European Record
K3 Immobilien AG and werke versorgung wallisellen ag (die werke) have put into operation the most profitable façade solar system in Europe in the new commercial building “K3 Handwerkcity”. The groundbreaking energy concept of the industrial park is being scientifically monitored by Empa. The aim is to make the industrial park as ecological and self-sufficient as possible.

