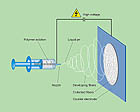
Electrospinning ultra thin polymer fibers
Spinning the finest fibers
Empa scientists have succeeded in constructing a spinning apparatus which is capable of producing polymer fibers with diameters in the nanometer range. The fibers and the machine that creates them will be on display and working at the NanoPubli stand at the Olma Fair in St. Gall from 13th to 15th September.

|
The polymer fibers produced
Continuous polymer fibers with diameters down to a few nanometers can be manufactured using electrospinning methods, but the product is usually in a disordered form. Empa researchers and technicians have therefore constructed a new spinning apparatus to improve this situation |
||
|
Accelerated, spun and stretched In the elecrospinning process, a high voltage is maintained between the spin nozzle and a counter electrode. The material to be spun, in the form of a solution, is forced under pressure through the nozzle, which is 400 to 700 microns in diameter. If the electric field is strong enough to overcome the surface tension of the emerging liquid, it is pulled into a fine jet that is accelerated towards the counter electrode, spun in the air and thereby drawn into long fibers. The solvent evaporates and the fibers collect on the counter electrode with a velocity of up to 100 meters per second. |
||
|
Although it sounds simple in principle, in reality the spinning process is quite complicated. Numerous parameters influence the process, including the concentration of the solution, the dielectric constant of the solvent, the strength and shape of the electric field and environmental conditions such as the relative humidity of the air. It demands experience and skill from the experimenter to adjust the process parameters so that fibers form and not just droplets, and on top of this for every new material a new set of optimal parameters must be established.
Filter systems for medicinal applications To date the Empa researchers have been able to successfully spin a number of polymers and other materials including polyamide, polyethylene oxide, polyvinyl pyrrolidone and wool protein in combination with polymers. The latter material can be used as a biocompatible substrate on which to grow cells. The current scientific task is to establish the optimal layout and operation of the apparatus in order to be able to spin fibers with complete control. A further aim is the manufacture of filters for medicinal applications, and for this purpose filter materials are given an additional coating of nano fibers. The electrospinning process is particularly suitable for this application since it takes place at room temperature. Heat -sensitive active agents can thus be directly mixed into the fibers that are then coated onto the filter materials. |
||
|
Author : Contact: |
||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||