Analysis of N2O isotopomeres and
the 18O isotopologue
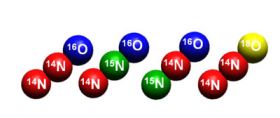
The natural abundance of 15N and 18O isotopes in nitrous oxide (N2O) as well as the 15N intramolecular distribution can be used to obtain important information on its geochemical cycle, because many biological and chemical processes lead to distinct isotopic signatures. N2O is a linear, non-symmetric molecule (N–N–O), with the four main isotopic species: 14N14N16O, 15N14N16O, 14N15N16O, and 14N14N18O. The nitrogen atom at the center (a site) and one at the end (b site) lead to two structural isomers, namely 14N15N16O and 15N14N16O, referred to as 15Na and 15Nb, respectively.
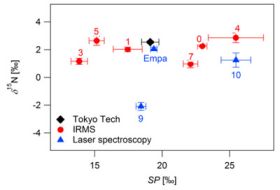
Employing recently available quantum cascade lasers (QCL) we are able to perform continuous and precise analysis of the isotope ratios d15N and d18O-N2O and the site-specific isotope ratios d15Na and d15Nb (e.g. Wächter et al. 2008). By coupling the QCL spectrometer to a fully-automated preconcentration unit we achieve quasi-continuous and high precision analysis of N2O isotopic species at ambient mixing ratios (Mohn et al. 2010, 2012,). In an inter-laboratory campaign we demonstrated excellent compatibility of QCL-based N2O isotopomer analysis with isotope-ratio mass-spectrometry (IRMS) for d15N and d18O and superior performance for d15Na and d15Nb (Mohn et al. 2014).

Applications include laboratory incubation experiments on soil, wastewater and aqueous solution to determine the site-specific isotopic signatures of distinct N2O source and sink processes. (Köster et al. 2013, Wunderlin et al. 2013, Heil et al. 2014). These source signatures in combination with ambient N2O isotopic time series are then used for source allocation and partitioning (Mohn et al. 2012, 2013, Harris et al. 2014). In a first long-term field campaign on an intensively managed grassland controls on N2O source processes were investigated based on their N2O isotopic composition (Wolf et al. 2014).
References:
- Wolf et al. 2015 First on-line isotopic characterization of N2O above intensively managed grassland. Biogeosci. 12(8), 2517-2531.
- Harris, E. et al. 2015 Nitrous oxide and methane emissions and nitrous oxide isotopic composition from waste incineration in Switzerland. Waste Manage. 35: 135-140.
- Harris, E. et al. 2015 Isotopic evidence for nitrous oxide production pathways in a partial nitritation-anammox reactor. Water Res. 83: 258-270.
- Mohn, J. et al. 2014 Interlaboratory assessment of nitrous oxide isotopomer analysis by isotope ratio mass spectrometry and laser spectroscopy: Current status and perspectives. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 28(18), 1995-2007.
- Harris, E. et al. 2014 Development of a spectroscopic technique for continuous online monitoring of oxygen and site-specific nitrogen isotopic composition of atmospheric nitrous oxide. Anal. Chem. 86(3), 1726-1734.
- Heil, J. et al. 2014 Site-specific 15N isotopic signatures of abiotically produced N2O. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 139, 72-82.
- Mohn, J. et al. 2013 N2O emissions and source processes in snow-covered soils in the Swiss Alps. Isotopes in Environ. Health Stud. 49(4), 520-531.
- Köster, J.R. et al. 2013 Novel laser spectroscopic technique for continuous analysis of N2O isotopomers - application and intercomparison with isotope ratio mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 27(1), 216–222.
- Wunderlin, P. et al. 2013 Isotope signatures of N2O in a mixed microbial population system: constraints on N2O producing pathways in wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47(3), 1339-1348.
- Mohn, J., et al. 2012 Site selective real-time measurements of atmospheric N2O isotopomers by laser spectroscopy. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 5, 1601–1609.
- Mohn, J. et al. 2010 A liquid nitrogen-free preconcentration unit for measurements of ambient N2O isotopomers by QCLAS. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 3, 609-618.
- Waechter, H. et al. 2008 Determination of N2O isotopomers with quantum cascade laser based absorption spectroscopy. Opt. Express 16(12), 9239-9244.
-
Share